Economic and Labour Situation in Japan, May 2024
Prime Minister Kishida Emphasizes Cooperation with RENGO for Wage Increases.
Prime Minister Fumio Kishida attended the RENGO (Japanese Trade Union Confederation) May Day Central Rally held in Tokyo on the April 27th. Regarding the 2024 spring labour–management negotiations (Shunto), he stated, “There is a strong trend of wage increases surpassing last year.” The Prime Minister’s attendance marks the second consecutive year, following his appearance in 2023.
The Prime Minister referred to the implementation of a fixed-amount tax reduction of 40,000 yen per person in June, emphasizing, “This year, we will definitely achieve income growth surpassing price increases. We will surely establish wage increases surpassing price increases from next year onwards.” He also said, “We will continue to listen to RENGO’s opinions and proceed with policies decisively and carefully in closer coordination.”
Tomoko Yoshino, President of RENGO, pointed out, “If the salaries of employees in small- and medium-sized enterprises, where 70% of workers are employed, do not increase, we cannot say that there is wage increase for everyone.” She urged for the establishment of the common business practice of appropriate price transfer including labour costs.
According to RENGO, the wage increase rate in the 2024 spring labour–management negotiations was 5.2% in the fourth tally of wage hike settlements. Compared to past final tallies of wage hike settlements, it reached the highest level since 1991.
Labour Force Survey Monthly Results*1
The average unemployment rate in fiscal 2023 remained unchanged from one year prior at 2.6%.
Japan’s job availability ratio in fiscal 2023 fell 0.02 points to 1.29 from the previous year, marking its first decline in three years, as companies curtailed recruiting practices amid pressure from rising materials costs.
(1) Employment
The number of employed persons in March 2024 was 67.26 million, an increase of 270,000 over the same month the previous year. By gender, this included 36.66 million men, up 60,000, and 30.60 million women, up 220,000 from the previous year.
(2) Unemployment
The number of unemployed persons in March 2024 was 1.85 million, an increase of 80,000 from the same month in the previous year.
The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate in March was 2.6%, unchanged from the previous month. The unemployment rate was 2.7% for men and 2.6% for women, unchanged from the previous month.
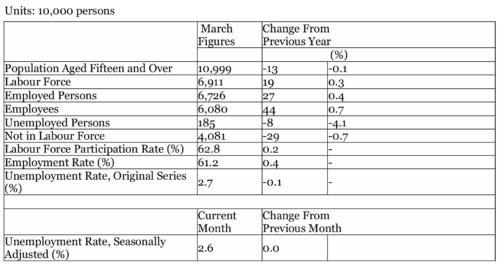
(3) Job Availability
Japan’s job availability in March stood at 1.28, up 0.02 points over the previous month. This ratio means there were 128 job openings for every 100 job seekers.
The ratio of regular employee job offers to applicants was 1.03, up 0.02 points over the previous month.
The ratio of new job offers to applicants, a leading indicator for the labour market, was 2.38, up 0.12 points over the previous month. The number of new job offers decreased 7.4%. By industry, scientific research, professional and technical services rose 1.6%. The manufacturing sector fell 10.8%, while living-related and personal services and amusement services dropped 10.5%.
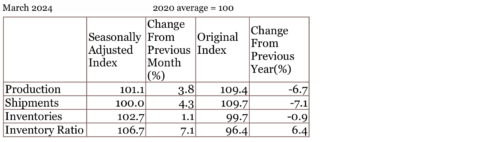
Industrial Production*2
Industrial output in March increased 3.8% from the previous month.
Production, shipments, inventories, and inventory ratio increased. The industries that mainly contributed to this increase were as follows: (1) motor vehicles; (2) production machinery; and (3) transport equipment (excl. motor vehicles), in that order.
According to the Survey of Production Forecasts in Manufacturing, production was expected to increase 4.1% in April and increase 4.4% in May.
Family Income and Expenditure Survey*3
(1) Expenditure of Households of Two Persons or More
Average monthly consumption expenditure of households of two or more persons in March was 318,713 yen, up 1.9% in nominal terms and down 1.2% in real terms from the previous year, declining for the 13th consecutive month.
(2) Income and Expenditures for Workers’ Households
Average monthly income per household stood at 513,734 yen, up 0.3% in nominal terms but down 0.1% in real terms from the previous year, due to higher inflation rates. The average level of consumption expenditure was 353,810 yen per month, up 4.1% in nominal terms and up 1.0% in real terms year-on-year.
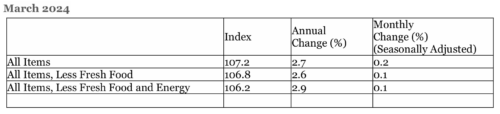
Consumer Prices*4
The consumer price index (CPI) in March was 107.2 (2020 = 100), up 2.7% over the previous year and up 0.2% over the previous month. Core inflation (CPI less food and energy) was up 2.9% over the previous year and up 0.1 over the previous month. Energy prices dipped 0.6%, as electricity bills fell 1.0% due to the government’s subsidization of utility bills for consumers. Food prices (excluding volatile fresh items) rose 2.6%. Accommodation fees jumped up 27.7%, as travel demand continued to recover with the return of foreign tourists to Japan.
<Y.A>
- Source: Labour Force Survey Monthly Results (Statistics Bureau of Japan) https://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/roudou/results/month/index.html
- Source: Indices of Industrial Production (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry)
https://www.meti.go.jp/english/statistics/tyo/iip/index.html - Source: Summary of the Latest Month on Family Income and Expenditure Survey (Statistics Bureau of Japan)
https://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/kakei/156.html - Source: Consumer Price Index (Statistics Bureau of Japan)
https://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/cpi/1581-z.html
https://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/cpi/1581-z.html
https://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/cpi/1581-z.html
